

Next: 2.3 Magnetic field
Up: 2. Governing equations
Previous: 2.1 Acoustic field in
In the case of linear elasticity and isotropic materials, the dynamic
behavior of mechanical systems can be described by the following
partial differential equation
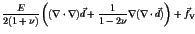 |
| |
= |
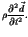 |
(4) |
In equation (4), E denotes the modulus of elasticity,  the Poisson's ratio,
the Poisson's ratio, 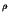 the density,
the density,
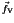 the
volume force and
the
volume force and 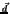 the mechanical displacement.
the mechanical displacement.
Martin Rausch
1999-04-08